
Singlestranded DNAbinding protein Stock Image C035/8205 Science
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) binding proteins (SSBs) are critical in maintaining genome stability by protecting the transient existence of ssDNA from damage during essential biological processes, such as DNA replication and gene transcription. The single-stranded region of telomeres also requires protection by ssDNA binding proteins from being.
Singlestranded Dnabinding Protein Photograph by Laguna Design/science
Using single-molecule imaging and manipulation, the authors show linker histone H1 preferentially forms phase-separated droplets with single-stranded nucleic acids over double-stranded DNA and.
DNA Replication
Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Proteins (SSBs) A.L. Eggler, in Encyclopedia of Genetics, 2001 Structure of SSBs: How Do They Bind DNA? SSBs from all organisms are, for the most part, functional homologs. Sequence similarity between various SSBs is limited; however, they share a DNA-binding motif called the OB fold.
PPT Chapter 10 Replication of DNA and Chromosomes PowerPoint
The recognition of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is integral to myriad cellular functions. In eukaryotes, ssDNA is present stably at the ends of chromosomes and at some promoter elements. Furthermore, it is formed transiently by several cellular processes including telomere synthesis, transcription, and DNA replication, recombination, and repair.

Solved Primer Lagging strand Primase Singlestranded binding
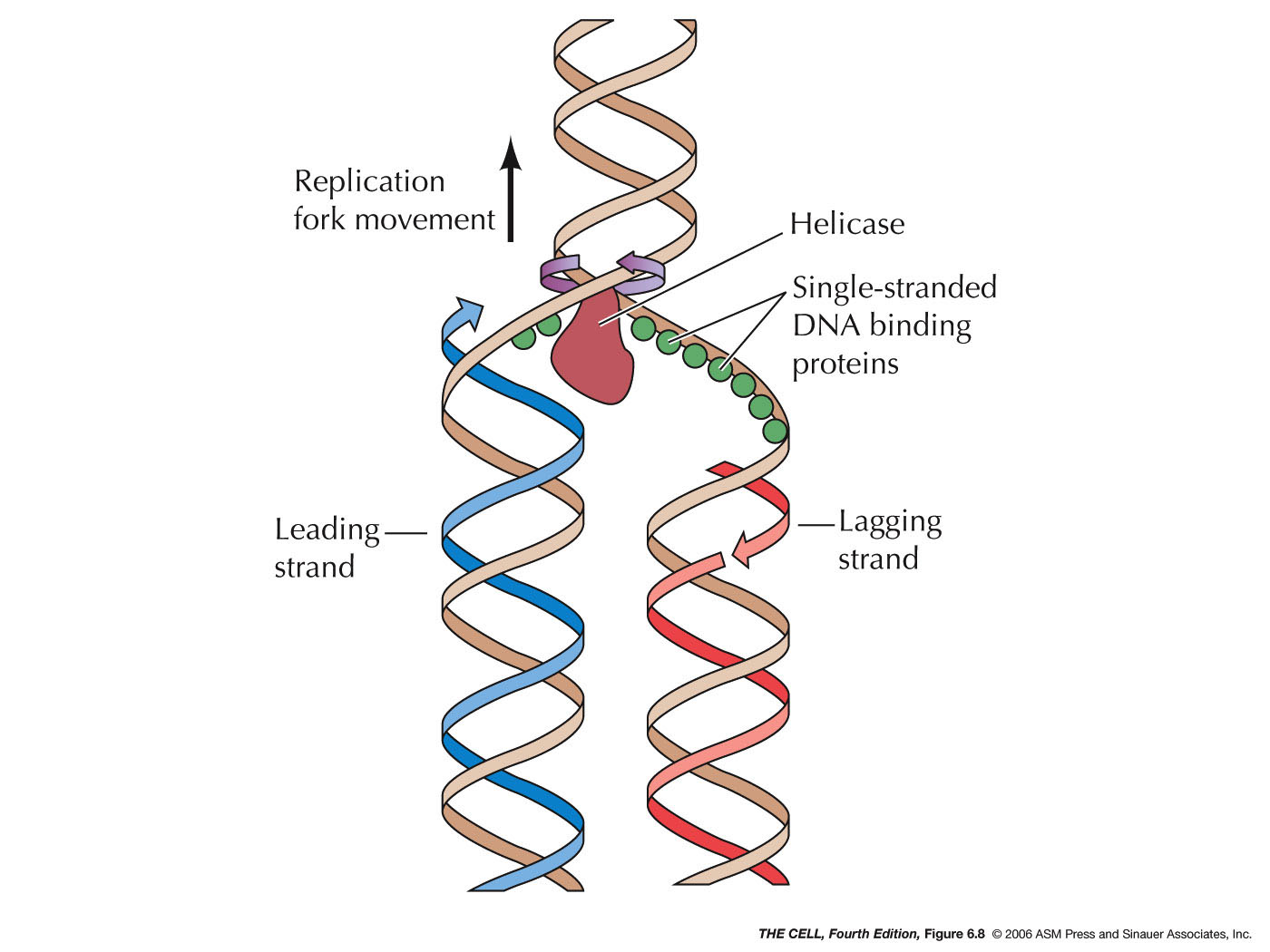
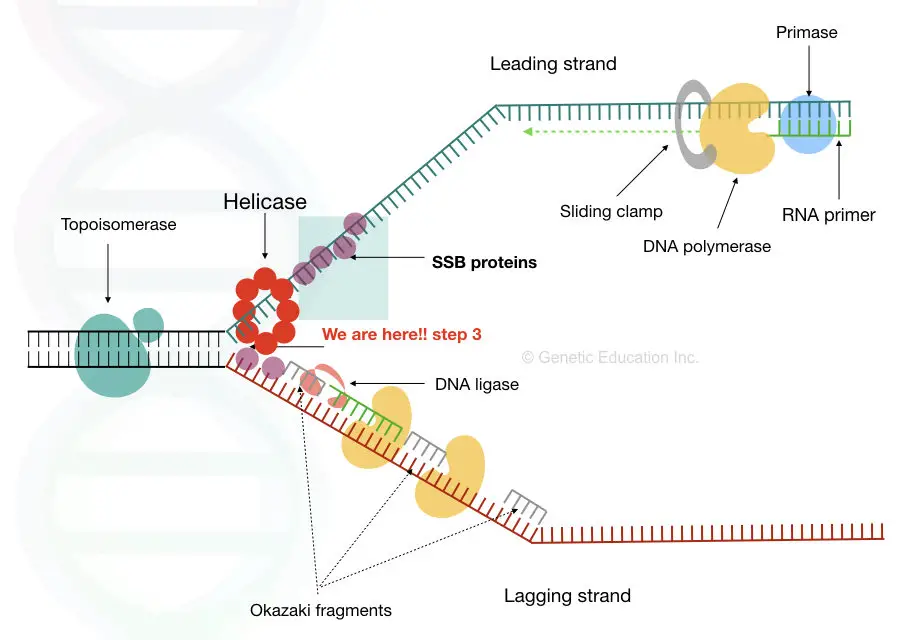
Single strand binding protein (ssb protein) binds to separated strands of DNA and prevents reannealing. Primase complexes with helicase, creates RNA primers (pppAC(N) 7-10) on the strands of the open duplex 2 (Primase+helicase constitute the Primosome).

TIFFANY'S BLOG
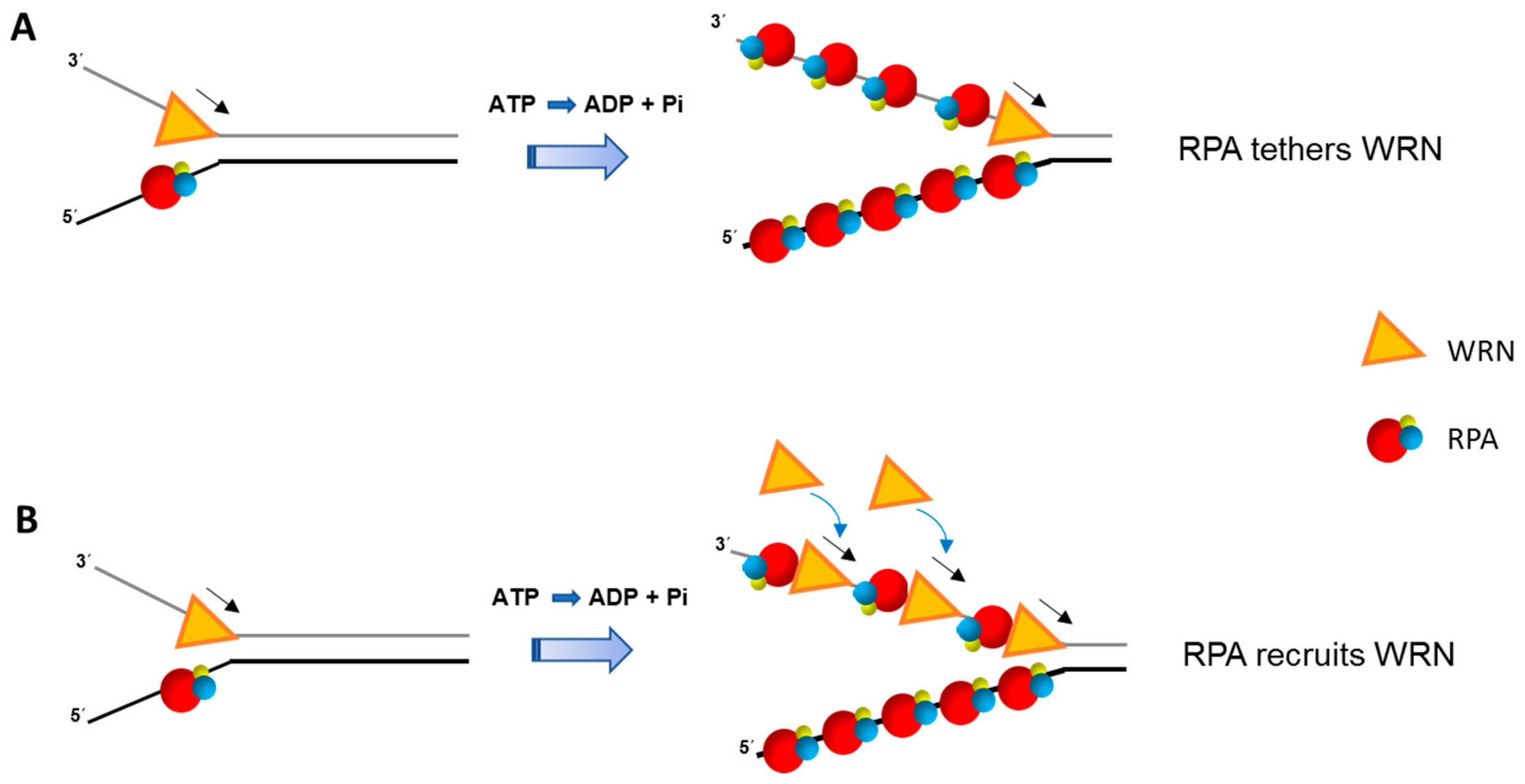
Biochemical study indicates that RPA can bind ssDNA in three states (illustrated in Figure 7 (b) ): (1) binding of OB folds A and B occludes about 10 nucleotides, (2) binding of OB folds A, B and C occludes 12-23 nucleotides, and (3) binding of the four OB folds occludes 28-30 nucleotides ( Arunkumar et al., 2003; Bastin-Shanower and Brill, 2001.
SingleStranded Binding Protein (SSB) Structure And Function
1. Introduction Central to many genome-maintenance machineries are single-stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBs). These SSB proteins play a vital role in the maintenance of genomes by binding exclusively and transiently to ssDNA intermediates during DNA replication, recombination, and repair.
IJMS Free FullText Interactive Roles of DNA Helicases and
In E. coli, this protein is a tetramer known as single-stranded-binding (SSB) protein, which the ssDNA winds itself around, while in T4 and T7, these proteins are monomers known as gp32 and gp2.5, respectively.

SingleStranded DNABinding Protein Interactions Keck Lab UWMadison
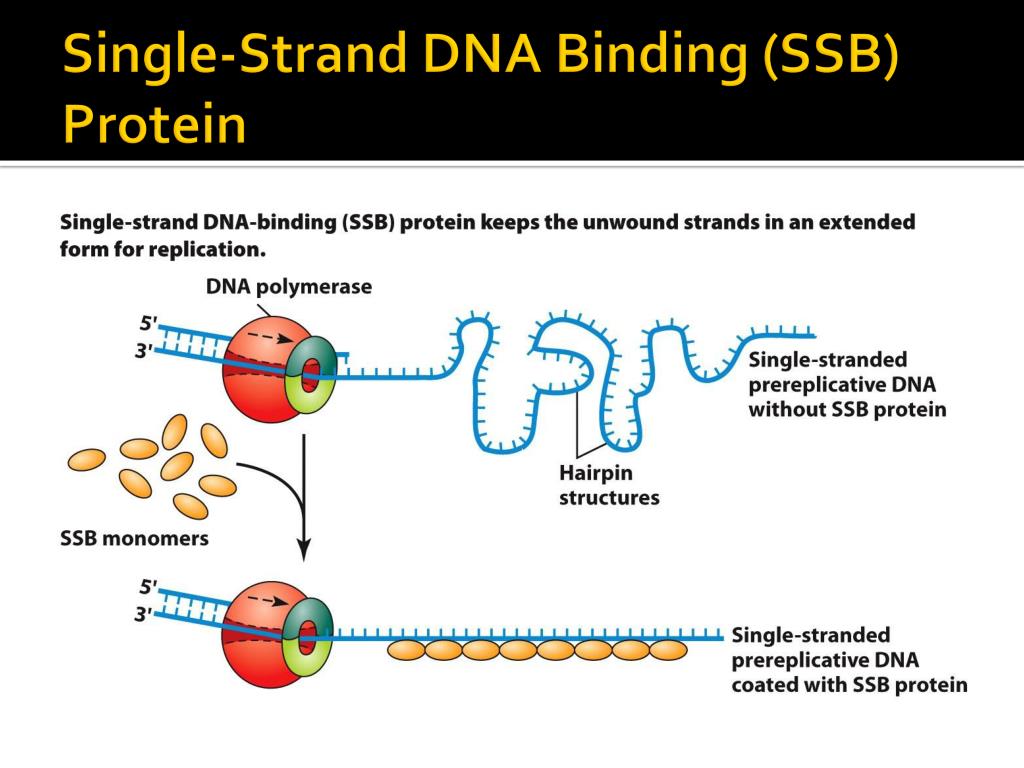
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in a cell is highly prone to degradation, so cells shield ssDNA from nucleases by coating it with ssDNA-binding proteins (SSBs). In eukaryotes, the canonical SSB is a.
Single Stranded Dnabinding Protein Photograph by Laguna Design/science
In one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during DNA replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or "old" strand and one "new" strand.

Structural dynamics of E. coli singlestranded DNA binding protein
Overview. Single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB) binds to single-stranded regions of DNA. This binding serves a variety of functions - it prevents the strands from hardening too early during replication, it protects the single-stranded DNA from being broken down by nucleases during repair, and it removes the secondary structure of the.

Peter Schmieder Intecation of singlestrand binding protein
Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA to prevent the helix from re-forming. Primase synthesizes an RNA primer. DNA polymerase III uses this primer to synthesize the daughter DNA strand. On the leading strand, DNA is synthesized continuously, whereas on the lagging strand, DNA is synthesized in short stretches called.

Singlestranded DNAbinding protein Stock Image C015/3229 Science
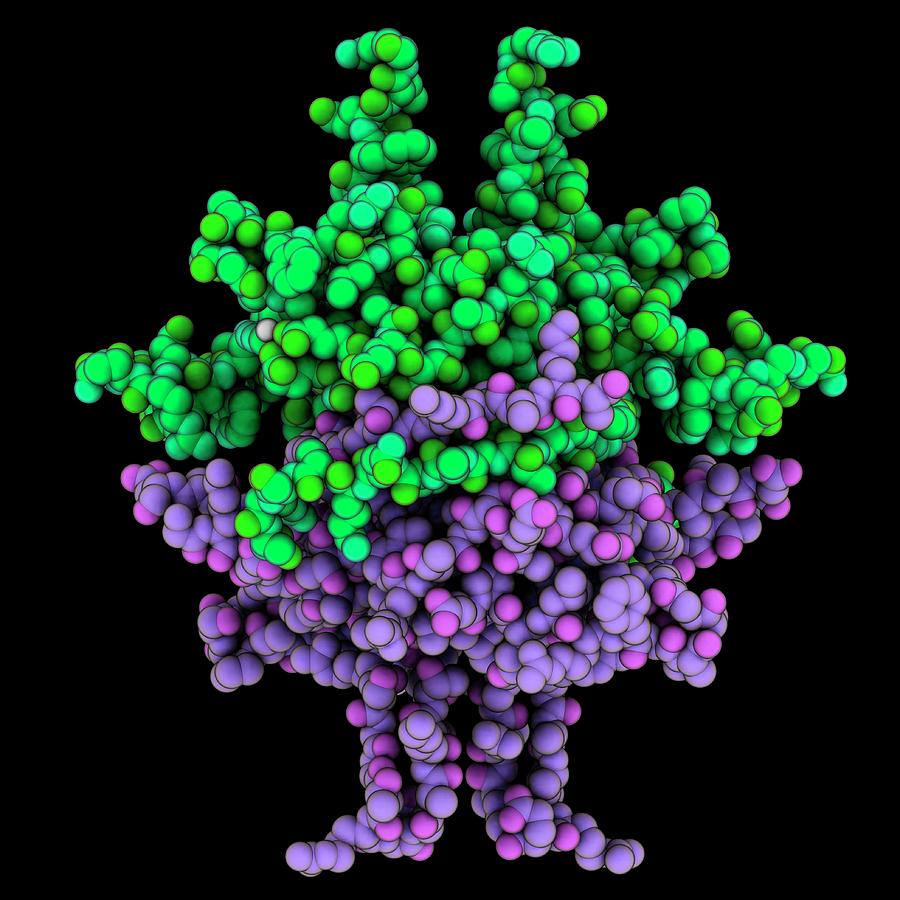
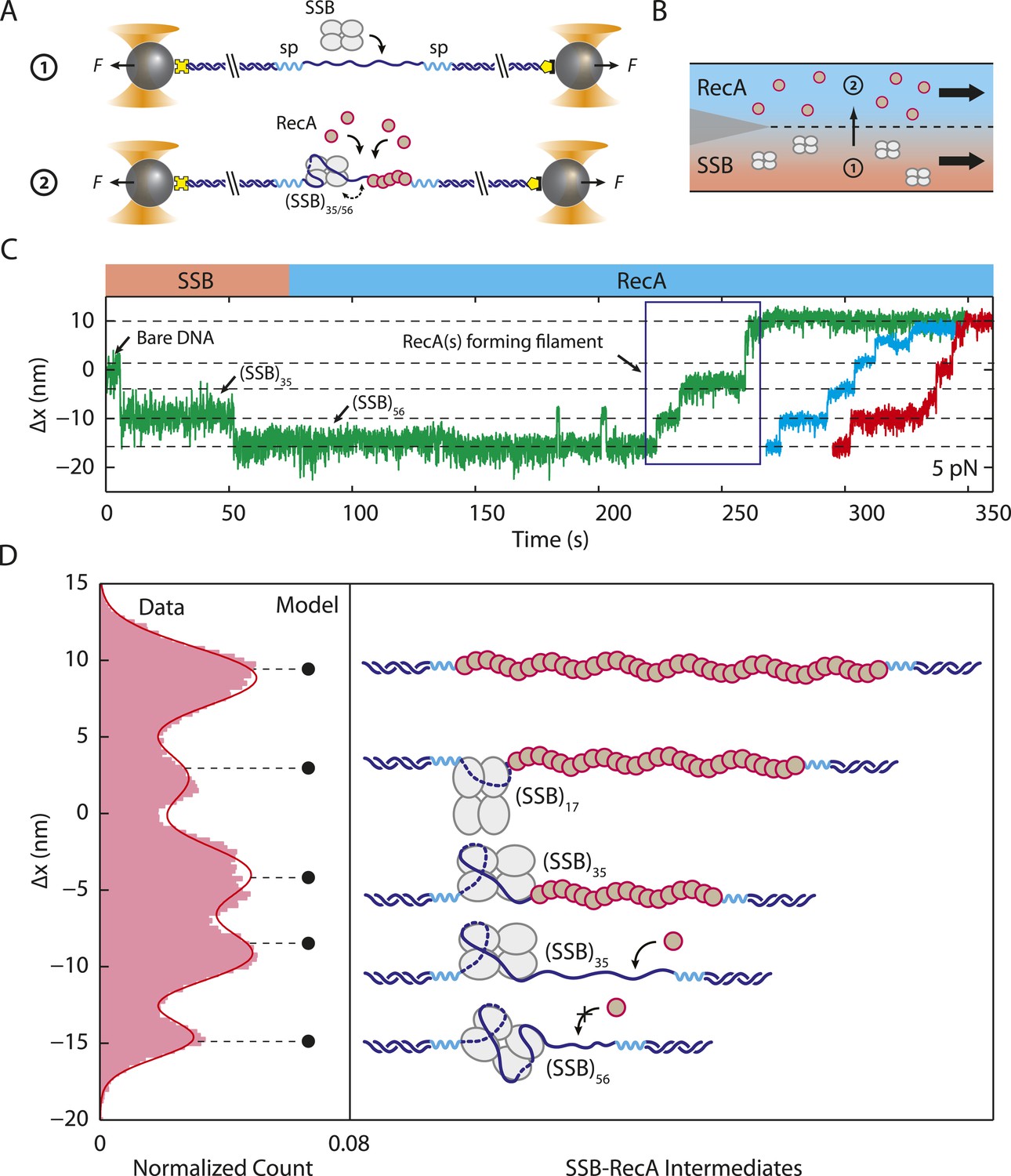
In bacteria, these proteins are known as single-stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBs) (7, 8). Escherichia coli SSB is a homotetramer, Figure 1A. Each monomer features a structured DNA-binding domain (residues 1-112) and a long and disordered C-terminal tail (residues 116-177) containing a highly acidic tip.

SingleStranded Binding Protein Structure And Function
The Escherichia coli single‐strand DNA binding protein (SSB) is essential to viability where it functions to regulate SSB interactome function. Here it binds to single‐stranded DNA and to target proteins that comprise the interactome. The region of SSB that links these two essential protein functions is the intrinsically disordered linker.

The three core proteins, singlestrand DNA binding protein
Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to keep the fork open. Primase synthesizes an RNA primer to initiate synthesis by DNA polymerase, which can add nucleotides only in the 5' to 3' direction. One strand is synthesized continuously in the direction of the replication fork; this is called the.
Structural dynamics of E. coli singlestranded DNA binding protein
Bacterial SSB proteins, as well as their eukaryotic RPA analogues, are essential and ubiquitous. They avidly bind single-stranded DNA and regulate/coordinate its metabolism, hence enabling essential DNA processes such as replication, transcription, and repair. The prototypic Escherichia coli SSB protein is encoded by an ssb gene.