
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in Singapore Dr Akash Verma
Nonidiopathic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis (non-IPF) describes a group of interstitial lung diseases (ILD) that cause inflammation and fibrosis of the lung interstitium, leading to impaired gas exchange due to a known cause. Depending on the specific disorder, it can also affect the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and pleura. Most of these diseases are characterized by clinical.
Difference between ELD and ILD Holland Aviation
Symptoms of interstitial lung disease. When you have interstitial lung disease, lung damage, irritation, and lack of oxygen can cause a variety of symptoms. These include: shortness of breath.
What are the different types of ILD? Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) Patient Education
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is an umbrella term used for a large group of diseases that cause scarring (fibrosis) of the lungs. The scarring causes stiffness in the lungs which makes it difficult to breathe and get oxygen to the bloodstream. Lung damage from ILDs is often irreversible and gets worse over time.
Factors Linked with Increased Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is an umbrella term that encompasses a large number of disorders that are characterized by diffuse cellular infiltrates in a periacinar location. The spectrum of conditions included is broad, ranging from occasional self-limited inflammatory processes to severe debilitating fibrosis of the lungs.

Pulmonary Hypertension With ILD Diagnostic and Treatment Challenges Pulmonology Advisor
Interstitial lung disease is the name for a group of 100 lung disorders that inflame or scar the lungs. The cause is not known. Major contributing factors are smoking and inhaling environmental or occupational pollutants. The most common symptoms are shortness of breath, especially with activity, and a dry, hacking cough.
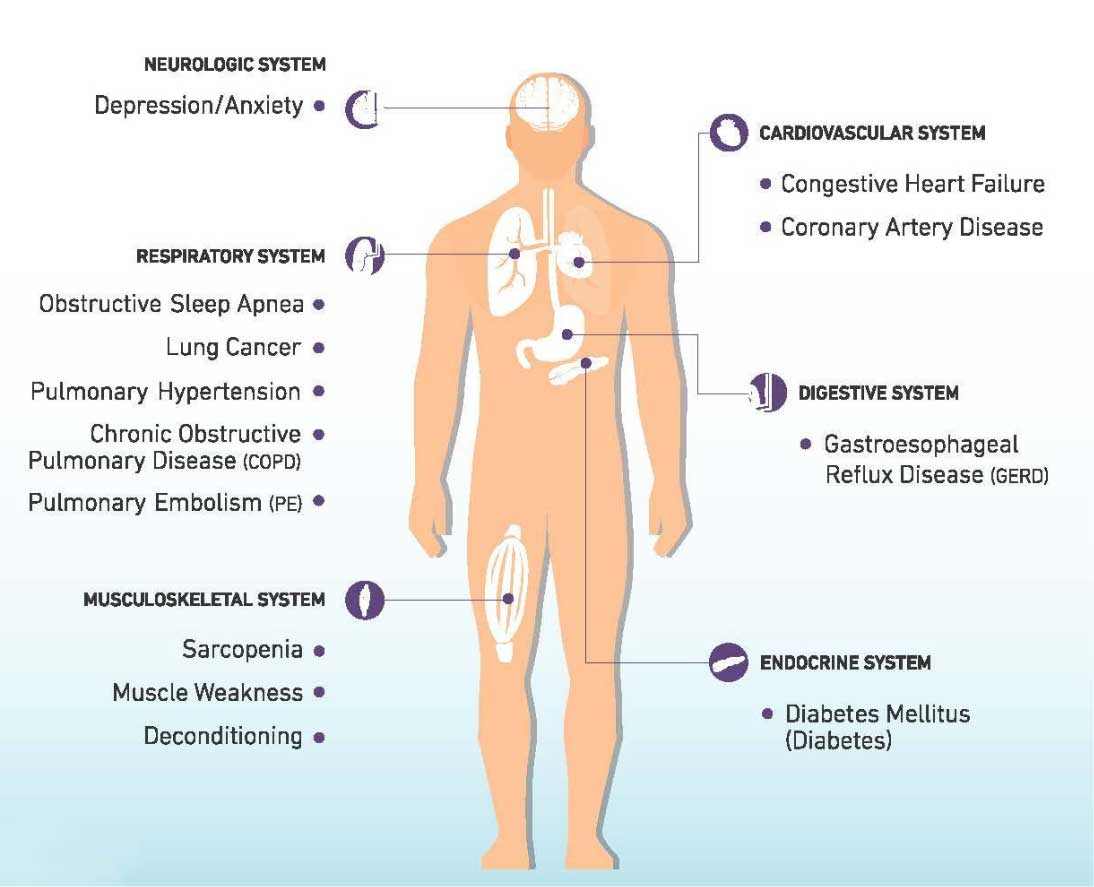
ILD Comorbidities CHEST
Rheumatoid arthritis. The prevalence of ILD in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is estimated at 5-10% and this figure is rising with the increasing screening of patients with RA [28-30].The predominant CT pattern is usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) followed by NSIP, the former of which confers a poorer prognosis [].The treatment of RA-ILD remains a poorly studied field, although it is widely.

Pathogenesis of SScILD and the various therapeutic targets Download Scientific Diagram
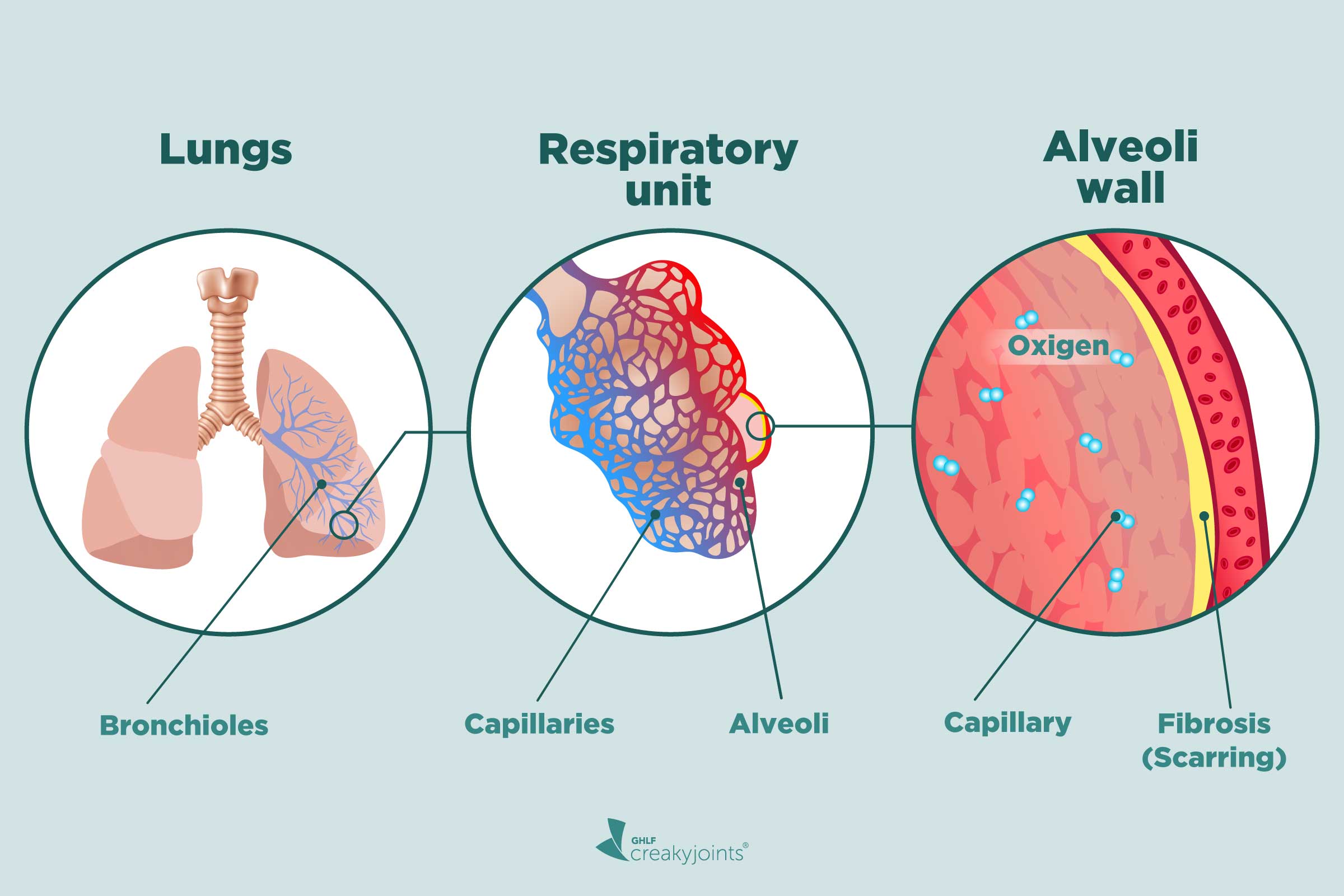
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a group of lung disorders in which the lung tissues become inflamed and then damaged. Alternative Names. Diffuse parenchymal lung disease; Alveolitis; Idiopathic pulmonary pneumonitis (IPP) Causes. The lungs contain tiny air sacs (alveoli), which is where oxygen is absorbed. These air sacs expand with each breath.
Monitoring of ILD progression Pulmonary Fibrosis 360
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal.
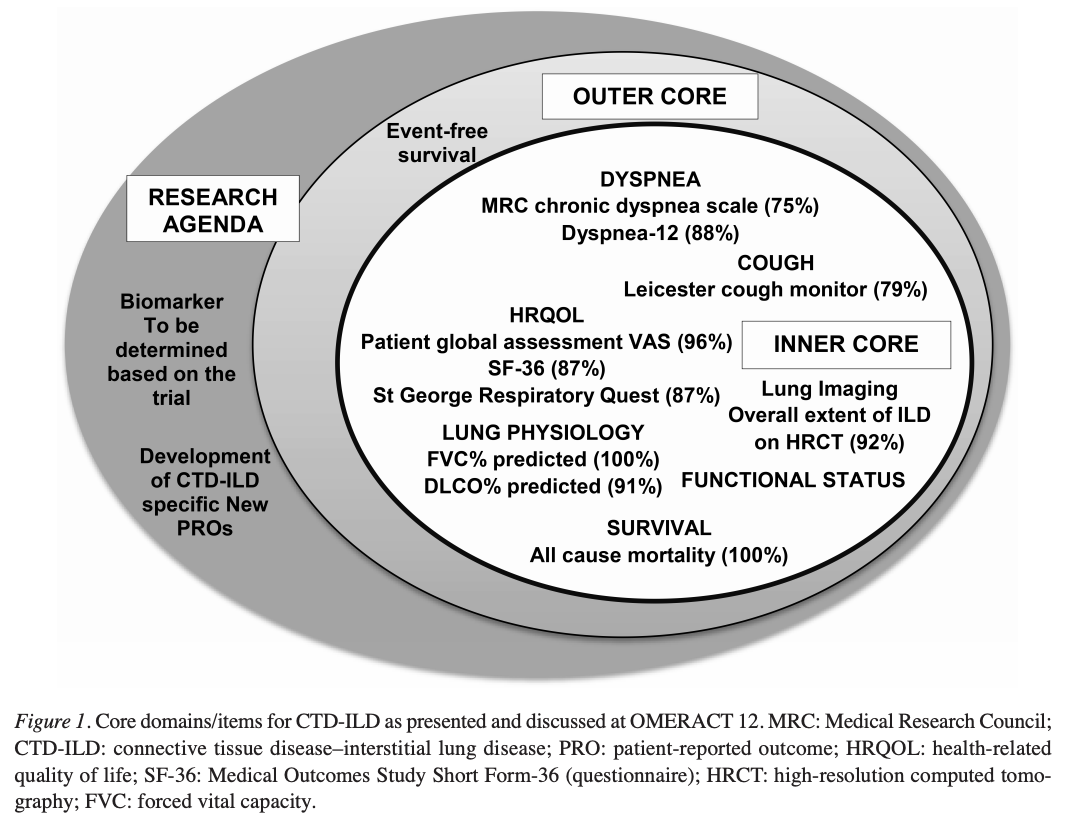
CTDILD OMERACT
Nintedanib is an intracellular inhibitor of tyrosine kinases. 7 Preclinical data have suggested that nintedanib inhibits processes involved in the progression of lung fibrosis. 7-11 In patients.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD)
Interstitial Lung Disease. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a term for a group of conditions that cause inflammation and scarring in your lungs. Symptoms of ILD include shortness of breath and a dry cough. ILD can be caused by medication, radiation therapy, connective tissue diseases or inhaling harmful substances.

CT findings and final diagnosis of group (I) ILD. Download Table
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), sometimes called diffused parenchymal diseases, describes a heterogeneous collection of distinctive lung disorders classified on the grounds of shared clinical, radiographic, physiologic or pathologic factors. What makes it difficult to understand this group of diseases is the confusing terminology. The pathogenetic sequence in actuality involves a series of.
What is ILD? Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) Patient Education
Interstitial lung disease adalah kelompok penyakit paru-paru yang ditandai oleh pertumbuhan jaringan parut atau fibrosis di paru-paru.Gejala penyakit ini antara lain batuk kering dan sesak napas yang dapat memburuk seiring waktu. Interstitial lung disease menyebabkan penebalan pada jaringan interstisial, yaitu jaringan di sekitar alveoli (kantung udara di paru-paru).

ILD Classification YouTube
The descriptive term "interstitial" reflects the pathologic appearance that the abnormality begins in the interstitium, but the term is somewhat misleading, as most of these disorders are also associated with extensive alteration of alveolar and airway architecture. An overview of the clinical findings that can aid in the diagnosis of ILD will.

Interstitial Lung Disease Symptoms and Treatment Healthsoul
Drug interactions that cause ILD have not been reported except in one case report by McFadden et al., who reported a case of "gold-naproxen pneumonitis." They hypothesized that naproxen interfered with the ability to restrain the immune response to gold, which resulted in clinical pneumonitis that resolved only when both naproxen and gold.

Chest Xray/ interstitial lung disease vs Pneumonia/Types of opacities in lungs YouTube
The field of interstitial lung disease (ILD) has undergone significant evolution in recent years, with an increasing incidence and more complex, ever expanding disease classification. In their most severe forms, these diseases lead to progressive loss of lung function, respiratory failure and eventually death. Despite notable advances, progress has been challenged by a poor understanding of.
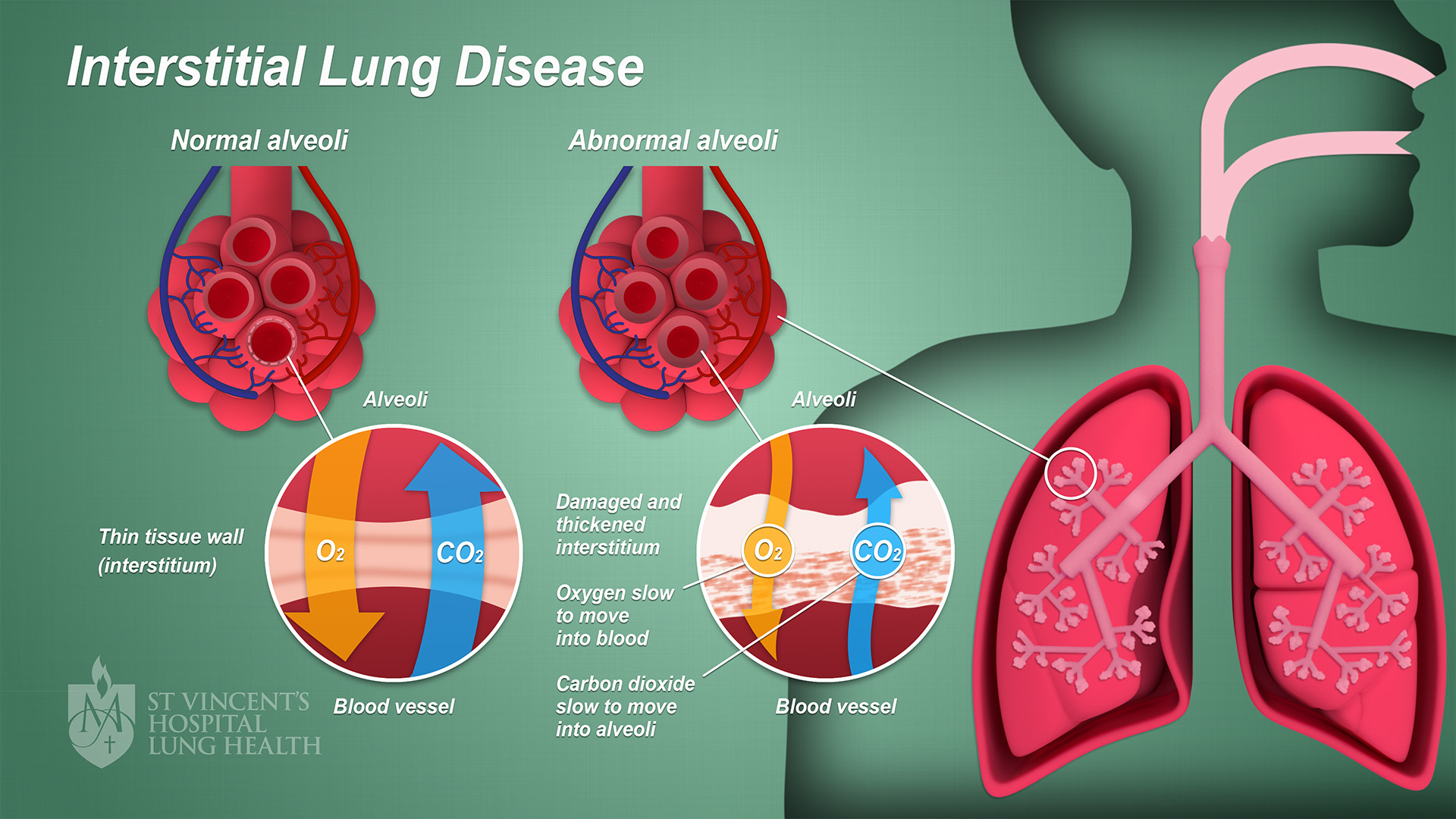
ILD JapaneseClass.jp
INTRODUCTION. Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD) is categorized as a smoking-related interstitial pneumonia and is one of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs) [].The other major IIPs include idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP; another smoking-related IIP), acute.